With the continuous attention to energy conservation, emission reduction, and environmental protection, various industries are actively exploring new technologies and methods to reduce energy consumption and environmental load. In this context, the exhaust heat recovery heat pump system has become a highly anticipated energy-saving and environmental protection tool.
The principle of exhaust heat recovery heat pump system
The waste heat recovery heat pump system mainly consists of a waste heat recovery device, a heat pump host, an evaporator, a condenser, an expansion valve, etc.
Waste heat recovery device: used to capture waste heat generated in industrial production processes, such as high-temperature heat in flue gas.
Heat pump host: It is an important component of the system, responsible for converting waste heat into usable heat energy. It includes components such as a compressor, condenser, evaporator, and expansion valve.
Evaporator: a component that converts a working fluid (such as refrigerant) from a liquid state to a gaseous state, absorbing heat during the evaporation process.
Condenser: a component that converts the working fluid from a gaseous state to a liquid state, releasing heat.
Expansion valve: used to control the flow and pressure of the working fluid, and regulate the working state of the system.
The working principle of the waste heat recovery heat pump system can be simply summarized as the following steps:
Waste heat recovery: The system first captures the high-temperature heat generated in industrial production, such as waste heat in flue gas, through a waste heat recovery device.
Evaporator heat absorption: The captured waste heat is used to heat the refrigerant in the evaporator, transforming it from a liquid to a gaseous state and absorbing heat.
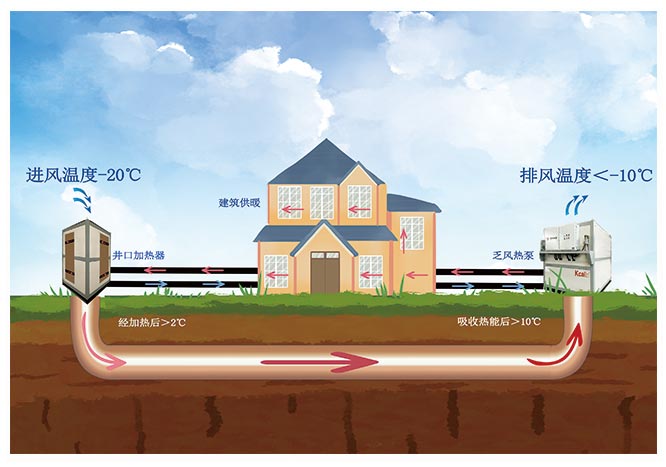
Compression raises temperature: The compressor compresses the refrigerant, increasing its temperature and pressure.
Heat release from the condenser: The compressed high-temperature and high-pressure refrigerant flows into the condenser, exchanges heat with the external environment, releases heat, and condenses into a liquid.
Expansion valve throttling: Liquid refrigerant relaxes through the expansion valve, reduces pressure and temperature, and re enters the evaporator cycle.
Through this cycle of operation, the waste heat recovery heat pump system can effectively convert the waste heat in the industrial production process into usable heat energy, achieving energy regeneration and utilization.
Advantages of waste heat recovery heat pump system for exhaust air
Energy conservation and emission reduction: The waste heat recovery heat pump system for exhaust air can effectively utilize the waste heat in industrial production processes, reduce dependence on traditional energy, and reduce emissions of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, which is in line with energy-saving and emission reduction policies and environmental protection requirements of enterprises.
Resource reuse: The system converts energy that was originally considered waste heat into usable thermal energy, achieving the reuse of resources. Not only does it save energy, but it also reduces the generation of waste and reduces its impact on the environment.
Improving energy utilization efficiency: By recycling waste heat, the system has improved the energy utilization efficiency in industrial production processes. Especially in cold seasons, the system can be used for heating, providing a stable source of thermal energy for production.
Economic benefits: Although the investment and construction of a waste heat recovery heat pump system may require certain costs, in the long run, the system can bring considerable economic benefits to enterprises by saving energy, reducing production costs, and obtaining environmental subsidies.
The exhaust heat recovery heat pump system, as a new type of energy-saving and environmental protection technology, has a simple and efficient principle. By effectively utilizing the waste heat generated in industrial production processes, the system has achieved the regeneration and utilization of energy, making important contributions to energy conservation, emission reduction, and environmental protection. With the continuous development and application of this technology, we believe it will play an increasingly important role in industrial production, helping us move towards a cleaner and more sustainable future.







Comment