As a key link in the energy industry, mines not only provide valuable mineral resources, but also conceal a precious and often overlooked treasure - waste heat from wind exhaustion. This type of waste heat resource is widely present inside mines, and in-depth analysis of its general temperature range and heat content is crucial for achieving sustainable energy utilization.
Temperature range of waste heat from exhaust air
The relationship between mine depth and temperature: Mine depth is one of the key factors affecting the temperature of exhaust heat. As the depth increases, the geothermal gradient gradually rises, leading to a corresponding increase in the temperature level inside the mine. Generally speaking, the deeper the mine, the wider the temperature range of exhaust heat.
Rock characteristics and temperature distribution: Different rock layers have differences in conduction, storage, and release of heat, which can also affect the temperature distribution of exhaust heat. Hard rock layers usually have low thermal conductivity, resulting in a slow temperature rise, while soft rock layers have relatively high thermal conductivity and a rapid temperature rise. Understanding the characteristics of rock layers helps to more accurately evaluate the temperature range of exhaust heat.
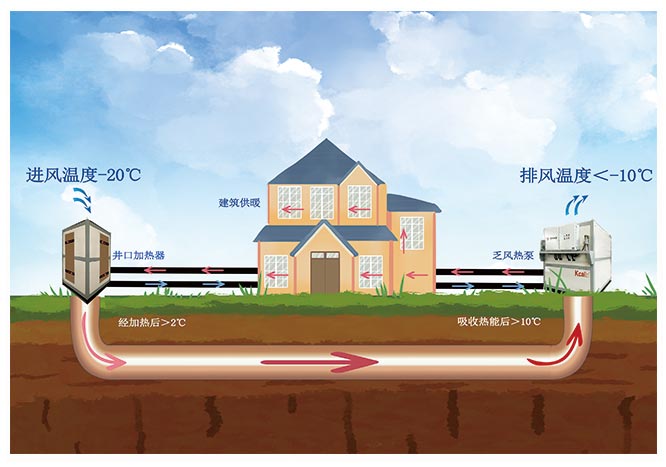
The heat content of waste heat from exhaust air
Heat source and content: The heat generated by the waste heat of the exhaust wind mainly comes from the geothermal energy inside the mine, friction of mechanical equipment, and natural radiation of ore. The heat from these sources accumulates in the mine and forms a potential energy source. The heat content varies with depth and changes in geological lithology, and for mining production, its heat potential is a resource worth further development.
Heat calculation and actual utilization: By accurately calculating the heat of waste heat from exhaust air, a reliable foundation can be provided for its actual utilization. The heat calculation of mine exhaust heat involves multiple aspects such as modeling the geothermal field and determining the thermal conductivity properties of rocks. At the same time, with the help of excellent thermodynamic technology, the total heat of exhaust heat in the mine can be more accurately evaluated.
Development and utilization of waste heat from exhaust air
Electricity generation: The temperature and heat content of mine exhaust heat make it an ideal source of electricity generation. Through thermal energy conversion technologies such as cogeneration and organic Rankine cycle, the waste heat of exhaust wind can be converted into electricity, providing renewable energy for mines and reducing energy costs.
Heating and cooling: The high-temperature part of the exhaust heat can be used for heating to meet the heating needs of the cold season in the mining area. Meanwhile, through heat pump technology, low-temperature waste heat from exhaust air can also be used for refrigeration, providing a comfortable working environment for mines.
Industrial heat: The high-temperature part of the waste heat from mine exhaust can be used for industrial heat, such as ore drying, slurry heating, etc. The endogenous nature of this energy makes its utilization an economically effective way to supplement energy in the mining production process.
The environmental potential of waste heat from exhaust wind
Greenhouse gas emission reduction effect: Using the waste heat of mine exhaust as an energy source can reduce greenhouse gas emissions compared to traditional coal or gas power generation methods, reduce the adverse impact of mines on the environment, and help achieve low-carbon economic goals.
Comprehensive utilization of resources: The development and utilization of waste heat from exhaust wind is a comprehensive utilization method of mining resources, which helps to achieve sustainable utilization of resources. This is in line with the pursuit of comprehensive resource utilization and sustainable development in modern society, and is of great significance for the sustainable development of the mining industry.
The temperature range and heat content of exhaust heat in mines are a vast and valuable energy resource, and their deep excavation and efficient utilization are crucial for promoting the sustainable development of the mining industry. Through scientific and technological means, combined with the concept of clean energy, mining enterprises are expected to find a new sustainable driving force in the treasure of waste heat from exhaust wind. With the joint efforts of continuously overcoming technical difficulties and improving policy systems, we have reason to expect that the waste heat from mine ventilation will inject more innovative vitality into the future energy field.







Comment